

₹ 1599.00
$149.00
GREEN HYDROGEN REVOLUTION
PART-1
FUELING TOMORROW

DOI – 10.61909/AMKEDTB092544
AUTHOR(S) -
MITALI KUSHWAHA, AMIT KUSHWAHA, ANIL CHOURASIYA
Genre/Subject – Green Energy, Green Hydrogen, Renewable Energy
Book code – AMKEDTB092544 pgs: 287
ISBN(P) – 978-93-6556-392-4
Published – 29/11/2025
ISBN(E) – 978-93-6556-966-7
Published – 22/09/2025
Edition – 1

AUTHORS

MITALI KUSHWAHA
With an illustrious career spanning 17 years, Mitali is a dynamic leader who marries her extensive expertise with an unwavering passion for innovation. Armed with a Master’s in Energy, Environment, and Management Engineering, along with a Bachelor’s in Electrical and Electronics Engineering, she represents the perfect fusion of technical prowess and environmental consciousness. As the visionary force behind her company, Mitali’s leadership fuels its journey towards sustainable excellence. Beyond her corporate role, she continues to actively contribute to academia and research, reflecting her commitment to advancing knowledge.

AMIT KUSHWAHA
With an impressive track record spanning over 15 years, Mr. Amit Kumar Kushwaha stands as a paragon of experience and innovation. Armed with a Master’s in Thermal Engineering and a Bachelor’s in Automobile Engineering, his expertise embodies a perfect synergy of technical brilliance and creative thinking. As the driving force behind his company, Amit’s dynamic leadership propels his team towards excellence. Beyond the boardroom, his fervent commitment to academia and research shines brightly. Active participation in scholarly pursuits reflects his dedication to ongoing learning and intellectual growth.

ANIL CHOURASIYA
Mr. Anil Chourasiya is a mechanical engineer and researcher specializing in Metal Matrix Composites, casting techniques, and sustainable manufacturing. With nearly six years of teaching and research experience, he has contributed significantly to the fields of aerospace alloys, hybrid composites, and tribology.
Currently serving in IES College of Technology, Bhopal, he has published in reputed Q1 and SCIE-indexed journals and authored Springer book chapters. His research combines innovation and practicality, particularly in developing advanced materials for aerospace and green technologies.
Mr. Chourasiya has also filed multiple patents related to alloy processing and advanced manufacturing techniques, reflecting his strong R&D orientation.
ABOUT BOOK / ABSTRACT
The world is entering a new era of energy transformation — one defined by the urgent pursuit of net-zero emissions and a decisive shift away from fossil fuels. At the center of this transition stands green hydrogen — a clean, versatile, and high-energy fuel that has the potential to redefine how industries, transportation systems, and entire economies operate.
The Green Hydrogen Revolution explores the science, technology, and global vision behind hydrogen’s rise as the fuel of the future. It traces the evolution of hydrogen energy, explains its production pathways, and reveals how innovations in electrolysis, renewable integration, and fuel cell technology are making large-scale hydrogen deployment both practical and sustainable.
This book provides a comprehensive foundation for understanding every dimension of green hydrogen — from production, storage, and distribution to its diverse applications in power generation, industry, and mobility. It also highlights the economic, policy, and environmental frameworks that are driving hydrogen’s adoption worldwide.
Beyond the technical details, The Green Hydrogen Revolution captures the global movement toward clean energy independence, illustrating how nations, researchers, and industries are uniting to create a carbon-neutral future. Through detailed analysis, real-world examples, and forward-looking perspectives, the book shows how hydrogen can serve as the missing link between renewable energy sources and a sustainable, circular economy.
Whether you are a student, researcher, policymaker, or energy professional, this book is designed to inform, inspire, and empower — offering both scientific depth and strategic vision.
The revolution has already begun — and green hydrogen stands at its very heart.
BOOK MAP
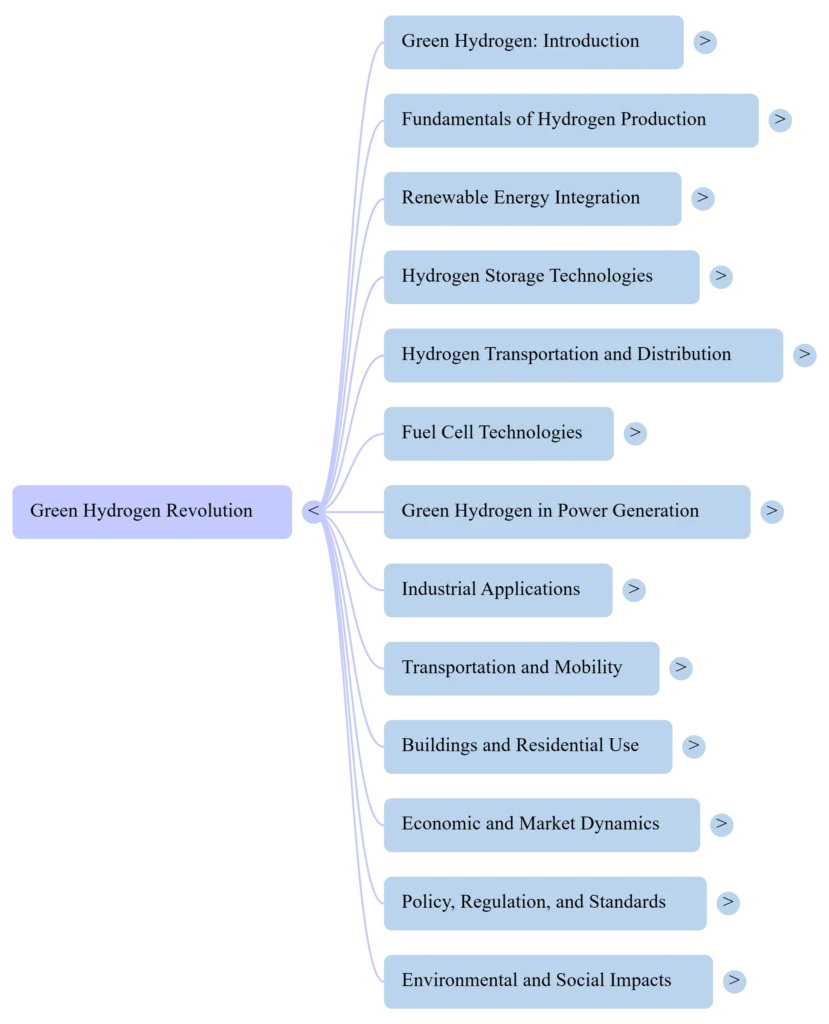
CHAPTERS
Chapter 1: Green Hydrogen: An Introduction |
1.1. Defining Green Hydrogen………………………………………. |
1.2. Historical Evolution of Hydrogen Energy……………………… |
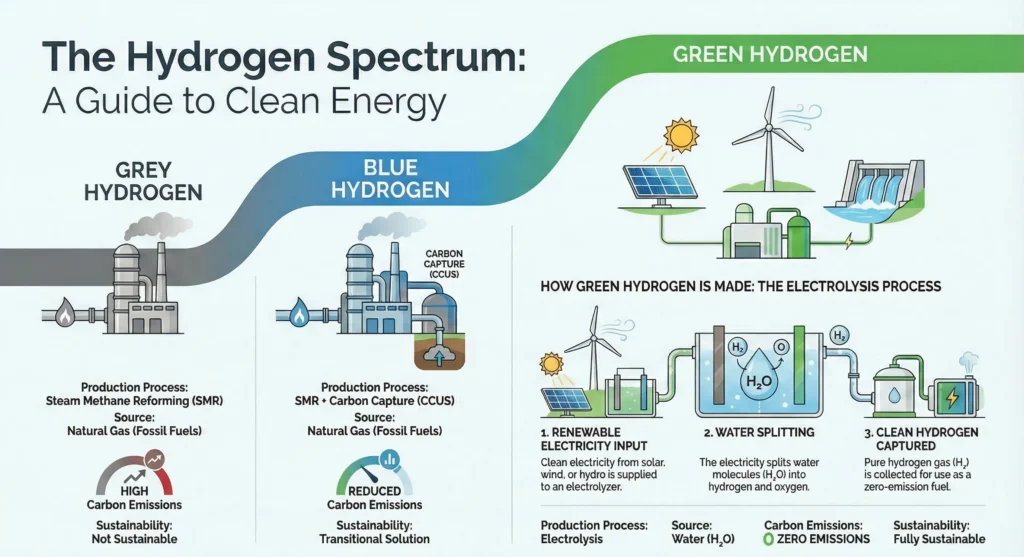
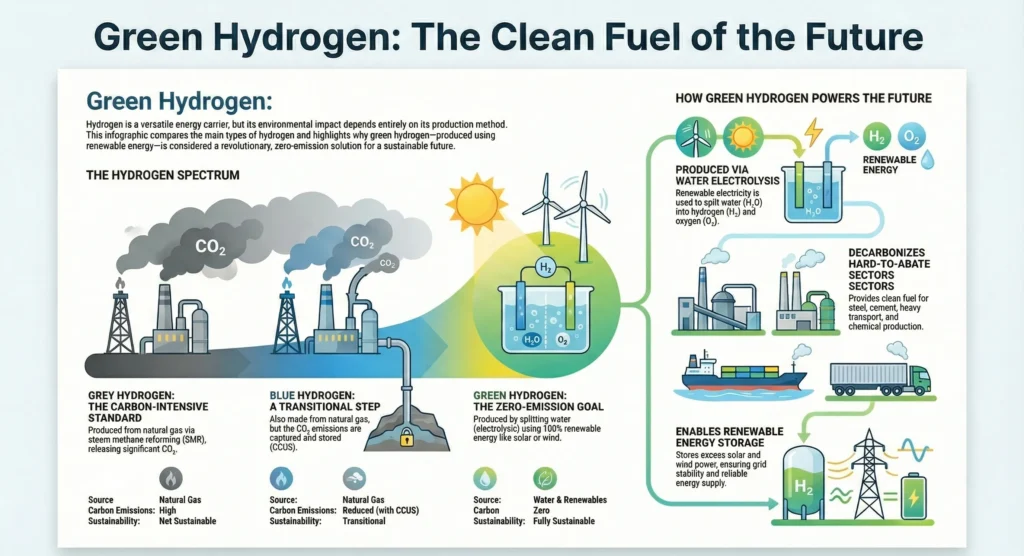
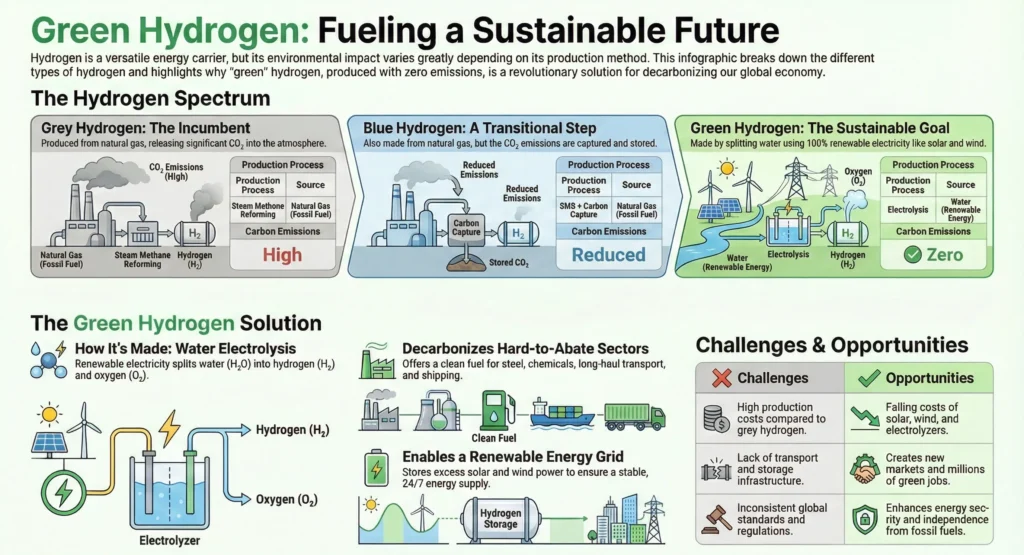
1.3. Comparison: Grey, Blue, and Green Hydrogen…………………. |
1.4. The Science of Water Splitting………………………………….. |
1.5. Global Drivers for Green Hydrogen Adoption………………….. |
1.6. Environmental Benefits and Carbon Reduction…………………. |
1.7. Key Challenges and Opportunities………………………………. |
|
Chapter 2: Fundamentals of Hydrogen Production…………… |
2.1. Electrolysis Principles…………………………………………… |
2.2. Types of Electrolyzers: Alkaline, PEM, AEM………………….. |
2.3. Thermochemical Processes……………………………………… |
2.4. Photocatalytic and Photoelectrochemical Methods……………… |
2.5. Biological Hydrogen Production………………………………… |
2.6. Energy Requirements and Efficiency Metrics…………………… |
2.7. Water Purity and Pre-treatment………………………………… |
2.8. Safety Considerations in Production……………………………. |
|
Chapter 3: Renewable Energy Integration……………………… |
3.1. Solar-to-Hydrogen Systems……………………………………… |
3.2. Wind-Powered Electrolysis………………………………………. |
3.3. Hybrid Renewable Configurations……………………………… |
3.4. Grid-Connected vs. Off-Grid Systems…………………………… |
3.5. Energy Storage Synergies……………………………………….. |
3.6. Demand Response and Load Balancing…………………………. |
|
Chapter 4: Hydrogen Storage Technologies……………………. |
4.1. Compressed Gas Storage………………………………………… |
4.2. Liquid Hydrogen Storage……………………………………….. |
4.3. Metal Hydrides and Chemical Carriers………………………… |
4.4. Cryogenic Storage Challenges…………………………………… |
4.5. Advanced Materials for Storage…………………………………. |
4.6. Safety and Leakage Mitigation…………………………………… |
4.7. On-site vs. Centralized Storage…………………………………. |
4.8. Lifecycle Analysis of Storage Options…………………………… |
4.9. Future Directions in Storage Research………………………….. |
|
Chapter 5: Hydrogen Transportation and Distribution………. |
5.1. Pipeline Infrastructure…………………………………………… |
5.2. Compressed and Liquefied Transport……………………………. |
5.3. Shipping and Maritime Carriers………………………………… |
5.4. Distribution Hubs and Refueling Stations……………………… |
5.5. Regulatory and Safety Standards……………………………….. |
5.6. Cost Analysis of Transport Modes………………………………. |
5.7. Infrastructure Challenges in Developing Regions………………. |
5.8. Innovations in Distribution Logistics…………………………… |
|
Chapter 6: Fuel Cell Technologies……………………………….. |
6.1. Fuel Cell Operating Principles………………………………….. |
6.2. Types: PEMFC, SOFC, AFC, MCFC…………………………… |
6.3. Component Materials and Catalysts……………………………. |
6.4. Performance Metrics and Efficiency…………………………….. |
6.5. Durability and Degradation Mechanisms………………………. |
6.6. System Integration and Balance-of-Plant……………………….. |
6.7. Cost Reduction Strategies……………………………………….. |
6.8. Emerging Fuel Cell Architectures………………………………. |
|
Chapter 7: Green Hydrogen in Power Generation…………….. |
7.1. Hydrogen Turbines and Combustion Engines………………….. |
7.2. Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems……………………… |
7.3. Integration with Renewable Power Plants………………………. |
7.4. Grid Stability and Ancillary Services…………………………… |
7.5. Microgrids and Distributed Generation…………………………. |
7.6. Pilot Projects and Demonstrators……………………………….. |
7.7. Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE) Analysis………………….. |
7.8. Policy Incentives and Market Mechanisms……………………… |
|
Chapter 8: Industrial Applications………………………………. |
8.1. Steel and Cement Decarbonization………………………………. |
8.2. Chemical and Ammonia Production…………………………….. |
8.3. Refining and Petrochemical Uses………………………………. |
8.4. Glass and Ceramic Industries…………………………………… |
8.5. Food Processing and Hydrogenation……………………………. |
8.6. Industrial Heat and Steam………………………………………. |
8.7. Economic Feasibility Assessments………………………………. |
|
Chapter 9: Transportation and Mobility………………………… |
9.1. Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)……………………………… |
9.2. Hydrogen for Heavy-duty Trucks and Buses……………………. |
9.3. Maritime and Shipping Applications……………………………. |
9.4. Aviation and Aerospace Prospects……………………………… |
9.5. Refueling Infrastructure and Networks…………………………. |
9.6. Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) with Hydrogen………………………….. |
9.7. Total Cost of Ownership Comparisons………………………….. |
9.8. Regulatory and Safety Considerations…………………………. |
|
Chapter 10: Buildings and Residential Use……………………. |
10.1. Residential Fuel Cells and Micro-CHP………………………… |
10.2. Hydrogen Blending in Natural Gas Networks………………… |
10.3. Backup Power and Off-Grid Solutions…………………………. |
10.4. Energy Efficiency and Building Integration…………………… |
10.5. Safety Standards for Residential Use………………………….. |
10.6. Pilot Projects and Living Labs…………………………………. |
10.7. Consumer Acceptance and Behavior…………………………… |
10.8. Business Models for Residential Hydrogen……………………. |
|
Chapter 11: Economic and Market Dynamics………………….. |
11.1. Global Hydrogen Market Overview…………………………… |
11.2. Cost Components and Economies of Scale…………………….. |
11.3. Pricing Mechanisms and Trading Hubs………………………. |
11.4. Investment Trends and Financing Models…………………….. |
11.5. Public-Private Partnerships……………………………………. |
11.6. Risk Analysis and Mitigation………………………………….. |
11.7. Market Forecasts and Scenarios……………………………….. |
11.8. Role of Carbon Pricing and Credits…………………………….. |
|
Chapter 12: Policy, Regulation, and Standards………………… |
12.1. International Hydrogen Roadmaps…………………………….. |
12.2. National and Regional Policies………………………………… |
12.3. Safety and Technical Standards………………………………… |
12.4. Incentives and Subsidies……………………………………….. |
12.5. Permitting and Regulatory Challenges………………………… |
12.6. Trade and Export Controls…………………………………….. |
12.7. Harmonization of Global Standards……………………………. |
12.8. Role of NGOs and Industry Consortia………………………… |
|
Chapter 13: Environmental and Social Impacts………………… |
13.1. Life Cycle Assessment of Hydrogen Systems………………….. |
13.2. Water Footprint and Resource Use…………………………….. |
13.3. Emissions and Air Quality Benefits……………………………. |
13.4. Social Acceptance and Community Engagement……………… |
13.5. Equity and Access Considerations……………………………… |
13.6. Environmental Justice Issues…………………………………… |
13.7. Circular Economy and Waste Management…………………… |
13.8. Biodiversity and Land Use Impacts……………………………. |





